

In the case of a double bond, there is one sigma bond and one pi bond.In the case of a single bond, there is only one sigma bond.Number of sigma and pi bonds in a molecule:.Usually p orbital takes part in pi-bond formation.Pi bonds are formed by side by side overlapping of atomic orbitals.Sigma bonds are the strongest covalent bond. For example, in structure I a carbon and a nitrogen are joined by a triple bond (that is, a sigma bond and two pi bonds), whereas in structure II the same atoms are joined by a double bond (that is, one sigma bond and one pi bond).Sigma bonds are formed by head-on overlapping of atomic orbitals.
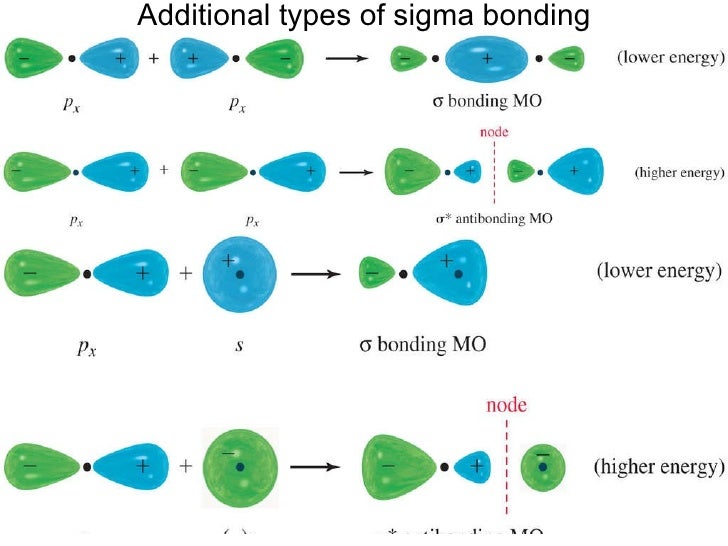
Pi Bonds play no role in determining a molecule’s shape. Sigma bonds play a role in affecting the shapes of molecules. The orbitals that overlap in a pi bond must be hybridized. The orbitals that overlap in a sigma bond can either be hybrid or pure. They are weak compared to the sigma bond. They have high energies and are stronger. P and d orbitals are included in the formation of pi bonds. S and p orbitals are included in the formation of sigma bonds. Pi Bonds can not exist without a sigma bond. Pi bonds are formed as a result of side-by-side overlapping of atomic orbitals. Sigma bonds are formed as a result of head-on-head overlapping of atomic orbitals. Atoms with incomplete p or d orbitals overlap and form pi bonds. are examples of molecules having pi bonds. Acrylonitrile (C3H3N), Ethylene (C2H4), etc. It is present in double and triple covalent bonds. The overlapping takes place in such a way that the axes of the atomic orbitals remain parallel to each other and perpendicular to the internuclear axis.”Ī pi bond is represented by the Greek letter π. Here, side by side overlapping takes place. ”Pi bonds are the result of the pairing of unbound p-orbital electrons between two atoms. When two fluorine atoms having opposite spins approach each other, their p orbitals overlap with each other. Here, the electronic configuration of fluorine is F: 1s 2 2s 2 2px 2 2py 2 2pz 1. In other words, a single bond cannot be a pi bond. Thus, a pi bond is always present in molecules with multiple bonds, i.e., double or triple bonds. The reason is that the atoms constituting a single bond prefer to form a strong sigma bond rather than a weak pi bond. The formation of fluorine (F 2) molecules is an example of the p-p sigma bond. A pi bond between two atoms is formed only in addition to a sigma bond. They can be formed by the overlap of the same orbitals or by overlap with different orbitals. p-p sigma bond (p-p overlapping): p-p sigma bond is formed when two atoms with half-filled p orbitals overlap. Sigma bond is formed by head-on the overlap of s-orbital. Sigma and Pi Bonds Linear: A triatomic molecule of the type AX2 that has its two bonding orbitals 180 apart, producing a molecule of linear geometry examples.In case of HF molecule, electronic configuration of hydrogen atom is H : 1s 1 and electronic configuration of fluorine is F : 1s 2 2s 2 2px 2 2py 2 2pz 1, which facilitates the formation of s-p sigma bond (provided the spin of electrons in overlapping orbitals is opposite). Examples of s-p sigma bonds include formation of HF molecule, H-X type molecules (HCl, HBr and HI). s-p sigma bond (s-p overlapping) : s-p sigma bond is formed when two atoms with one having half-filled s orbital and another having half-filled p orbital overlap. In Sigma bond the electron density is maximum and it is cylindrically symmetrical about the bond axis.There are three types of overlapping in sigma bonds: are some examples of molecules having sigma bonds.
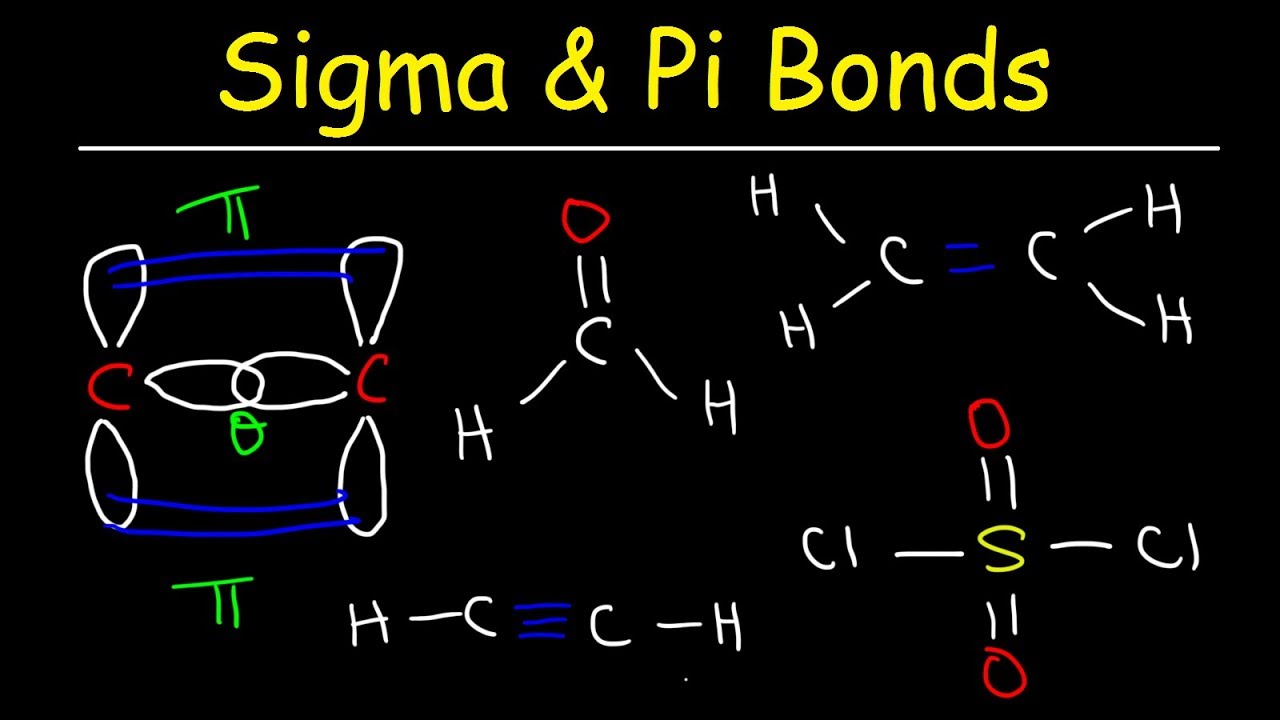
Sigma bonds are the strongest covalent bonds and they are formed as a result of head-on overlapping of orbitals.

For example, in a covalent molecule C 2H 4, there are 5 sigma bonds and one pi bond. Atoms with incomplete s or p orbital with opposite spins overlap and form sigma bonds (the strongest bond). It is present in single, double, and triple covalent bonds. With respect to rotation about the bond axis, it is symmetrical.”Ī sigma bond is represented by the Greek letter σ. \) molecule.“Sigma bonds are the result of head-on overlapping that takes place between atomic orbitals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
